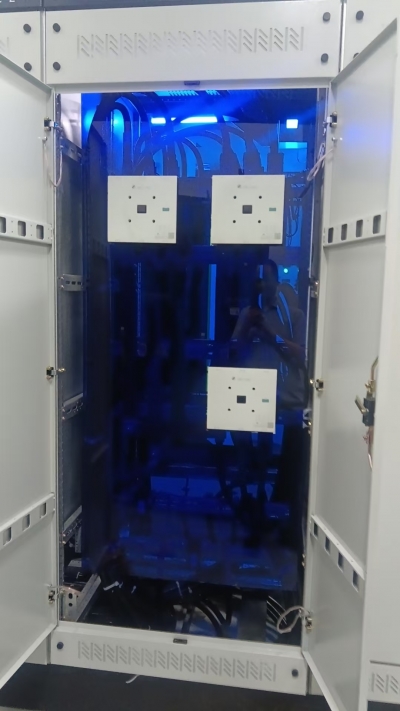
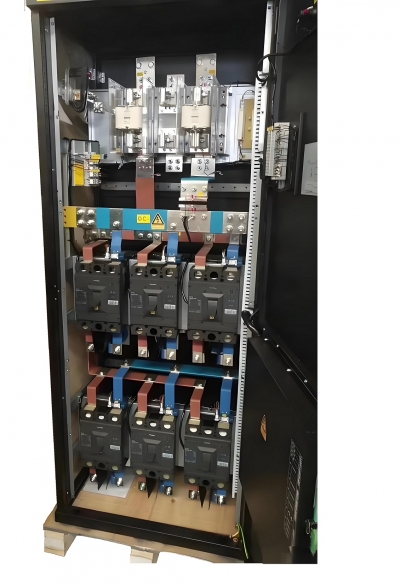
#1. Core functions of DC low-voltage distribution cabinet
The main functions of a DC low-voltage distribution cabinet include the following aspects:
(1) Energy allocation: Distribute direct current from the power source to different electrical devices according to demand, ensuring the balance of power supply.
(2) Circuit protection: By using devices such as circuit breakers and fuses, it prevents damage to equipment and personnel caused by overload, short circuits, and other faults.
(3) Monitoring and Control: Equipped with voltage and current monitoring instruments to monitor the real-time operation status of the system, facilitating timely detection and handling of problems by operation and maintenance personnel.
(4) Modular design: Modern DC low-voltage distribution cabinets usually adopt a modular structure, which is easy to expand and maintain, and can adapt to different scales of electricity demand.
#2. Application scenarios of DC low-voltage distribution cabinets
Due to its high efficiency and stability, DC low-voltage distribution cabinets have been widely used in multiple fields:
(1) Photovoltaic power generation system: In solar power plants, DC distribution cabinets are used to collect the DC electricity generated by photovoltaic modules and transmit it to inverters or energy storage systems.
(2) Data center: Data centers require extremely high stability in power supply, and DC distribution can reduce conversion links and improve energy efficiency.
(3) Electric vehicle charging facilities: Some fast charging stations use
DC power supply, and distribution cabinets play a key role in such scenarios.
(4) Industrial automation: Automation equipment in factories often requires a stable
DC power supply, and distribution cabinets can meet this demand.
With the popularization of renewable energy and energy storage technology, the market demand for DC low-voltage distribution cabinets will continue to grow.
#3. Future Development Trends of DC Low Voltage Distribution Cabinets
With the advancement of technology and the adjustment of energy structure, the development of DC low-voltage distribution cabinets presents the following trends:
(1) Intelligent upgrade: In the future, distribution cabinets will integrate more intelligent monitoring functions, such as remote monitoring, fault warning, etc., to improve operation and maintenance efficiency.
(2) Energy efficiency optimization: By improving materials and design, further reducing electrical energy loss and enhancing the overall energy efficiency of the system.
(3) Standardization and compatibility: The industry will promote more unified standards to ensure seamless integration of devices from different manufacturers and facilitate system integration.
#4. How to choose a suitable DC low-voltage distribution cabinet
When choosing a DC low-voltage distribution cabinet, the following factors should be considered:
(1) Load demand: Select the appropriate distribution cabinet specifications based on the power and voltage requirements of the electrical equipment.
(2) Safety certification: Ensure that the product meets relevant safety standards, such as fire prevention, electric shock prevention, and other requirements.
(3) Scalability: If future electricity demand may increase, distribution cabinets with modular expansion capabilities should be selected.
(4) After sales service: Choose a reputable supplier to ensure timely technical support for the equipment during use.
#Conclusion
As an important component of modern power systems, the performance of DC low-voltage distribution cabinets directly affects the stable operation of electrical equipment. With the continuous advancement of technology, DC distribution systems will play an important role in more fields. The continuous innovation of enterprises such as Kyushu Electric has injected new vitality into the development of this industry. For users, understanding the basic principles and application scenarios of DC low-voltage distribution cabinets can help make more reasonable equipment selection decisions, thereby improving the overall efficiency and reliability of the power system.





 New Energy Wind and Solar Storage Project Engineering
New Energy Wind and Solar Storage Project Engineering
 Stage rental and distribution areas
Stage rental and distribution areas
 LED display screen and lighting engineering
LED display screen and lighting engineering
 Smart industrial control
Smart industrial control
 Low voltage distribution system
Low voltage distribution system
 Operation and maintenance management system of Internet of things
Operation and maintenance management system of Internet of things









